Proactive patch management is no longer a luxury but a necessity for enterprise businesses. Outdated software leaves critical vulnerabilities exposed, making organizations susceptible to devastating cyberattacks, data breaches, and significant financial losses.
Choosing the right patch management tool is crucial for maintaining a secure and efficient IT infrastructure. This in-depth guide explores some of the best patch management tools available in 2024, helping enterprise organizations make informed decisions based on their specific needs and resources. We’ll examine key features, benefits, drawbacks, and deployment options to ensure you select the perfect solution to safeguard your valuable assets.
Why Patch Management is Important
Application patch management is the process of updating software to address bugs and security vulnerabilities. It’s a critical service that every enterprise business needs. Keeping applications up-to-date is paramount for both security and performance, especially for foundational applications such as web servers, file transfer systems, and databases. Effective patch management minimizes the risk of exploitation by malicious actors and ensures optimal system performance. Failing to implement a robust patch management strategy can lead to significant consequences, including:
- Increased vulnerability to cyberattacks: Outdated software is a prime target for hackers, exposing your systems to malware, ransomware, and other threats.
- Data breaches and loss of sensitive information: Exploited vulnerabilities can lead to unauthorized access to sensitive data, resulting in significant financial and reputational damage.
- System downtime and disruptions: Bugs and vulnerabilities can cause system instability, leading to costly downtime and disruptions to business operations.
- Non-compliance with industry regulations: Many industries have strict regulations regarding data security and software updates. Failure to comply can result in hefty fines and legal repercussions.
How to Select the Right Patch Management Tool
Our selection process considered several critical factors to ensure we recommend only the most effective and reliable patch management solutions for enterprise businesses:
- Security: The tool must be inherently secure, resistant to hacking and corruption.
- Automation: The tool should automate the entire patching process, including scheduling, deployment, and reporting.
- Operating System and Application Support: Broad compatibility with various operating systems (Windows, macOS, Linux) and a wide range of third-party applications is essential.
- Scalability: The solution must scale efficiently with the organization’s growth, handling an increasing number of endpoints and applications without performance degradation.
- User-Friendliness: An intuitive interface that provides clear visibility into patch status and compliance is crucial for efficient management.
- Free Trial/Demo: The availability of a free trial or demo allows for thorough evaluation before committing to a purchase.
- Value for Money: The cost-effectiveness of the tool relative to its features and capabilities.
Top Patch Management Tools for Enterprise Businesses
The following section details some of the leading patch management tools available, categorized for easier comparison:
1. ManageEngine Patch Manager Plus (EDITOR’S CHOICE)
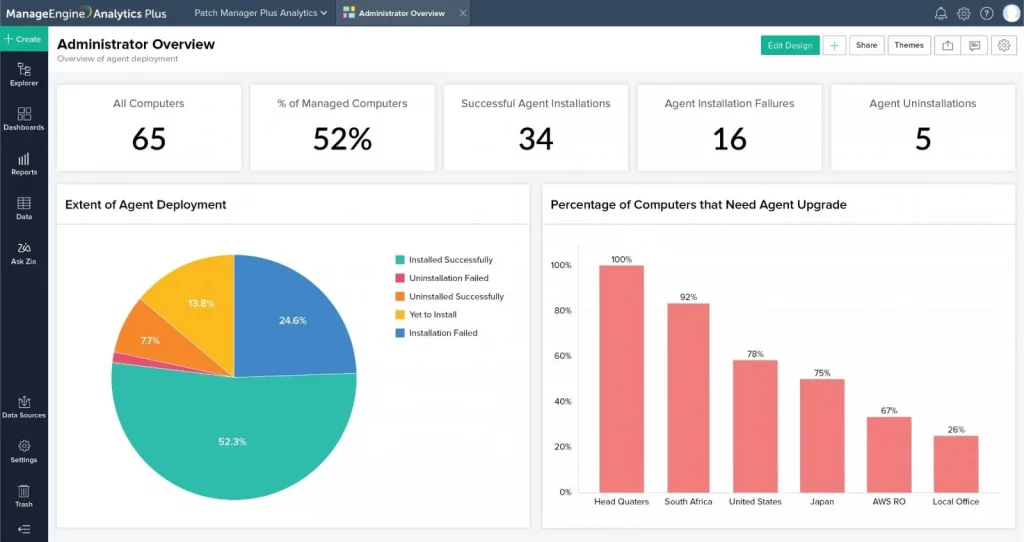
- Key Features: Multi-platform support (Windows, macOS, Linux), third-party application patching (over 850 applications), automated patch deployment, patch testing and approval workflows, role-based access control.
- Why We Recommend It: ManageEngine Patch Manager Plus excels in automation and streamlining the patching process, reducing manual workload and enhancing security. It offers flexibility, detailed reporting, and automated rollback/retry options.
- Target Audience: Medium to large businesses with complex IT infrastructures. A free edition is available for smaller businesses (up to 20 workstations and 5 servers).
- Pros: User-friendly interface, customizable notifications, patch delays and rollbacks, compliance auditing, cloud-based and on-premise deployment options.
- Cons: Limited third-party application patching for niche software.
- Pricing: Available as a software package for Windows Server and as a cloud-based SaaS package. A 30-day free trial of the Professional Edition is available.
2. NinjaOne Patch Management (FREE TRIAL)
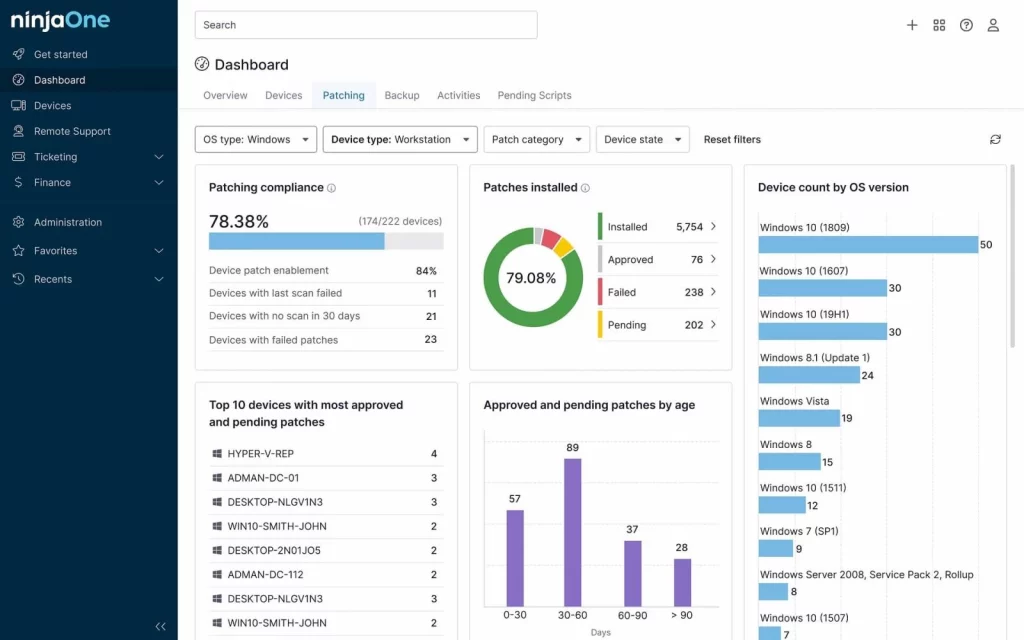
- Key Features: Multi-platform patching (Windows, macOS), third-party application patching (Adobe, Chrome, etc.), customizable patch approval policies and scheduling, detailed patching reports.
- Why We Recommend It: NinjaOne Patch Management is highly intuitive, cloud-based, and easy to deploy, making it ideal for MSPs and SMBs. Its unified platform increases IT efficiency.
- Target Audience: Small to medium-sized businesses and managed service providers (MSPs).
- Pros: Patch testing environment, integration with other NinjaOne tools, MSP-friendly features.
- Cons: Limited Linux support.
- Pricing: Cloud-based solution; a 14-day free trial is available.
3. Ivanti Endpoint Security for Endpoint Manager
- Key Features: Cross-platform patching (Windows, macOS, Linux), third-party application patching (Adobe, Java, etc.), patch automation, vulnerability remediation.
- Why We Recommend It: Ivanti Endpoint Security prioritizes security with vulnerability assessment and remediation. Its integration with the Ivanti ecosystem streamlines patching.
- Target Audience: Mid-to-large enterprises with complex IT infrastructures and strict compliance requirements.
- Pros: Vulnerability remediation, role-based access control, compliance features.
- Cons: Complex initial setup.
- Pricing: On-premises package for Windows Server; no free trial, but a demo is available.
4. SolarWinds Patch Manager
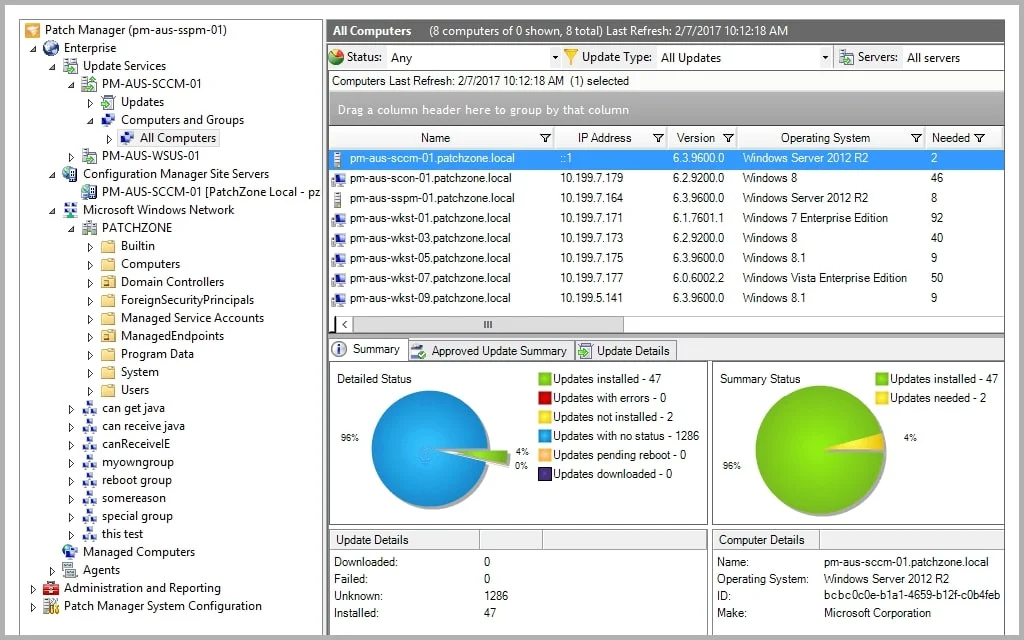
- Key Features: Integration with Microsoft WSUS and SCCM, automated processes, comprehensive third-party application patching.
- Why We Recommend It: SolarWinds Patch Manager enhances WSUS and SCCM functionalities, offering robust automation and reporting.
- Target Audience: Medium to large enterprises already using WSUS or SCCM.
- Pros: Activity logging, customizable alerts, advanced patch testing.
- Cons: Dependency on WSUS/SCCM.
- Pricing: Software package for Windows Server; a 30-day free trial is available.
5. GFI LanGuard
- Key Features: Patch management, vulnerability assessment (60,000+ vulnerabilities), compliance reporting.
- Why We Recommend It: GFI LanGuard offers a comprehensive approach to network security, combining vulnerability assessment, patch management, and reporting.
- Target Audience: Small to medium-sized businesses (SMBs) and enterprises seeking a closed-loop automated solution.
- Pros: Network scanning, agent and agentless options, centralized dashboard.
- Cons: No SaaS version (on-premises software package).
- Pricing: Software package for Windows Server; a demo is available, followed by a 30-day free trial.
6. SecPod SanerNow
- Key Features: Vulnerability management, patch management, compliance management (HIPAA, PCI, ISO, NIST).
- Why We Recommend It: SecPod SanerNow integrates vulnerability and patch management, automating scans, deployments, and reporting.
- Target Audience: Small to large enterprises with diverse IT environments and stringent security requirements.
- Pros: Asset management, endpoint management, integrated dashboard.
- Cons: Stronger at managing Windows; may require customization for specific environments.
- Pricing: Cloud-based SaaS package; a 30-day free trial is available.
7. Kaseya VSA
- Key Features: Remote monitoring and control, patch management, network monitoring.
- Why We Recommend It: Kaseya VSA offers comprehensive IT management capabilities, streamlining operations and enhancing security.
- Target Audience: Managed service providers (MSPs) and IT departments in SMBs and enterprises.
- Pros: Antivirus/antimalware, process automation, backup and recovery.
- Cons: Patch manager is part of a wider RMM tool; no Linux support.
- Pricing: SaaS platform; a demo is available.
Detailed Comparison of Top Patch Management Tools:
To further assist in your decision-making process, let’s delve into a more detailed comparison of the top patch management tools discussed earlier. This comparison will highlight key differentiators and help you identify the best fit for your enterprise’s specific requirements.
| Feature | ManageEngine Patch Manager Plus | NinjaOne Patch Management | Ivanti Endpoint Security | SolarWinds Patch Manager | GFI LanGuard | SecPod SanerNow | Kaseya VSA |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Deployment | On-premises, Cloud (SaaS) | Cloud (SaaS) | On-premises | On-premises | On-premises | Cloud (SaaS) | Cloud (SaaS) |
| OS Support | Windows, macOS, Linux | Windows, macOS | Windows, macOS, Linux | Windows | Windows/Server | Windows, macOS, Linux | Windows, macOS |
| Application Support | 850+ Third-party apps | Several key apps (Adobe, Chrome, etc.) | Several key apps | Several key apps | Many | 550+ Third-party apps | Several key apps |
| Automation | High | High | High | High | High | High | High |
| Reporting | Detailed, Customizable | Detailed | Detailed | Detailed | Detailed | Detailed | Detailed |
| Vulnerability Assessment | Integrated | Integrated (within NinjaOne platform) | Integrated | Integrated (via WSUS/SCCM) | Integrated | Integrated | Integrated (within Kaseya platform) |
| Integration | Integrates with other ManageEngine products | Integrates with other NinjaOne tools | Integrates with Ivanti ecosystem | Integrates with WSUS/SCCM | N/A | N/A | Extensive RMM integrations |
| Pricing Model | Subscription, Free Edition | Subscription | Subscription | Subscription | Subscription | Subscription | Subscription |
| Free Trial | 30-day free trial | 14-day free trial | Demo available | Demo available | Demo available, then 30-day trial | 30-day free trial | Demo available |
Choosing the Right Patch Management Tools:
The table above provides a clearer picture of the strengths and weaknesses of each tool. Here’s a breakdown to help you choose:
- For enterprises needing comprehensive, multi-platform support with strong automation and reporting: ManageEngine Patch Manager Plus is an excellent choice. Its robust features and flexible deployment options make it suitable for diverse IT environments.
- For smaller businesses or MSPs seeking a user-friendly, cloud-based solution: NinjaOne Patch Management offers ease of use and integration within its RMM platform.
- For large enterprises with complex IT infrastructures and stringent security requirements: Ivanti Endpoint Security, with its integrated vulnerability management capabilities, is a powerful solution.
- For organizations already using WSUS or SCCM: SolarWinds Patch Manager enhances these existing systems, providing advanced patching features and reporting.
- For businesses prioritizing a closed-loop automated solution: GFI LanGuard offers a comprehensive approach to network security, combining vulnerability assessment, patch management, and reporting.
- For enterprises needing a cloud-based solution with strong vulnerability and patch management integration: SecPod SanerNow is a robust option with compliance capabilities.
- For MSPs or enterprises requiring a comprehensive RMM solution with integrated patch management: Kaseya VSA provides extensive IT management capabilities.
Beyond the Tools: Implementing a Successful Patch Management Strategy
Selecting the right tool is only one part of the equation. A successful patch management strategy requires a holistic approach:
- Develop a comprehensive patching policy: This policy should define which systems need patching, the frequency of updates, the approval process, and procedures for testing and rollback.
- Prioritize critical systems: Focus on patching systems that hold sensitive data or are critical to business operations first.
- Implement a robust change management process: Ensure that all patches are tested thoroughly in a controlled environment before deployment to production systems.
- Regularly review and update your patching policy: The threat landscape is constantly evolving, so your policy needs to adapt accordingly.
- Provide adequate training to your IT staff: Ensure that your team is properly trained on using the chosen patch management tool and following established procedures.
- Monitor and report on patch compliance: Regularly monitor patch compliance levels and generate reports to track progress and identify any gaps in coverage.
By combining the right tools with a well-defined strategy, enterprise businesses can significantly reduce their vulnerability to cyberattacks, improve system performance, and maintain compliance with industry regulations. Remember to leverage free trials and demos to thoroughly evaluate the tools before making a final decision. The investment in a robust patch management system is a critical step towards safeguarding your organization’s valuable assets and ensuring its long-term success.
Conclusion
Selecting the best patch management tool for your enterprise depends on several factors, including your budget, IT infrastructure complexity, and specific security needs. Carefully consider the features, pros, and cons of each tool before making a decision. Remember that a robust patch management strategy is a cornerstone of a comprehensive cybersecurity plan, protecting your valuable assets and ensuring business continuity.
FAQs
Q: What are the best patch management tools for enterprise businesses?
A: The best patch management tools for enterprise businesses vary depending on specific needs, but top contenders include ManageEngine Patch Manager Plus, NinjaOne Patch Management, Ivanti Endpoint Security, SolarWinds Patch Manager, GFI LanGuard, SecPod SanerNow, and Kaseya VSA. Each offers unique strengths and weaknesses.
Q: How do I choose the right patch management tools for my enterprise?
A: Consider factors like scalability, automation capabilities, supported operating systems and applications, integration with existing systems, user-friendliness, and cost-effectiveness when selecting a patch management tool. A free trial or demo is highly recommended.
Q: What are the key considerations when choosing the best patch management tools for my enterprise’s specific needs?
A: Choosing the best patch management tools requires careful consideration of several factors:
- Scalability: The tool must handle your current workload and scale efficiently as your organization grows, managing increasing numbers of endpoints and applications.
- Integration: Assess how well the tool integrates with your existing IT infrastructure, including other security tools, monitoring systems, and ticketing systems. Seamless integration streamlines workflows and reduces complexity.
- Automation Capabilities: Prioritize tools that automate as much of the patching process as possible, from scheduling and deployment to reporting and compliance tracking. Automation reduces manual effort and minimizes human error.
- Reporting and Analytics: Robust reporting features are crucial for tracking patch compliance, identifying vulnerabilities, and demonstrating compliance to auditors. Look for tools that provide customizable reports and dashboards.
- Support and Training: Consider the level of support and training offered by the vendor. Reliable support is vital for resolving issues and ensuring smooth operation.
- Cost: Evaluate the total cost of ownership, including licensing fees, implementation costs, and ongoing maintenance. Balance cost with the features and benefits offered.
- Security: The tool itself must be secure and resistant to attacks. Look for tools with robust security features and a proven track record of reliability.
Q: How much does a good patch management tool cost for an enterprise?
A: The cost of enterprise-grade patch management tools varies significantly depending on the vendor, the number of endpoints managed, the features included, and the deployment model (cloud-based vs. on-premises). Pricing models typically involve subscription fees based on the number of managed devices or users. Expect to invest a substantial amount, as the cost is justified by the protection of critical systems and the prevention of costly downtime and security breaches. Requesting quotes from multiple vendors is crucial to compare pricing and features effectively. Remember to factor in implementation and training costs as well.
Q: Are cloud-based patch management tools better than on-premises solutions?
A: The best deployment model (cloud-based vs. on-premises) depends on your specific needs and infrastructure. Cloud-based solutions offer advantages such as scalability, accessibility, and reduced infrastructure management overhead. However, on-premises solutions might be preferred for organizations with strict data sovereignty requirements or concerns about network connectivity. Consider factors like security, compliance, and IT expertise when making your decision.
Q: What are some common mistakes to avoid when implementing a patch management solution?
A: Common mistakes to avoid include:
- Underestimating the scope of the project: Thoroughly assess your IT infrastructure and application landscape before selecting a tool.
- Failing to prioritize critical systems: Focus patching efforts on systems that hold sensitive data or are crucial to business operations.
- Insufficient testing: Always test patches in a controlled environment before deploying them to production systems to minimize the risk of disruptions.
- Lack of communication and training: Ensure that your IT staff is properly trained on using the chosen tool and that clear communication channels are established.
- Ignoring compliance requirements: Ensure that your patch management strategy aligns with relevant industry regulations and standards.
- Not regularly reviewing and updating your patching policy: The threat landscape is constantly evolving, so your policy needs to be regularly reviewed and updated.









