A devastating PSAUX ransomware attack has crippled over 22,000 CyberPanel instances, exploiting critical vulnerabilities in the software to encrypt data and demand ransoms. The attack highlights the severe consequences of unpatched software and underscores the importance of robust security practices.
Vulnerabilities Expose Thousands of Servers
Security researcher DreyAnd uncovered three significant vulnerabilities in CyberPanel versions 2.3.6 and likely 2.3.7. These flaws allowed attackers to gain unauthorized root access without authentication. The vulnerabilities included:
- Defective Authentication: CyberPanel’s decentralized authentication system left pages like ‘upgrademysqlstatus’ vulnerable to unauthenticated access. This meant attackers could bypass login procedures and access sensitive server functions.
- Command Injection: The lack of proper input sanitization on unprotected pages allowed attackers to inject and execute arbitrary system commands, essentially giving them complete control over the server.
- Security Filter Bypass: The security middleware only filtered POST requests, enabling attackers to bypass it using other HTTP methods like OPTIONS or PUT.
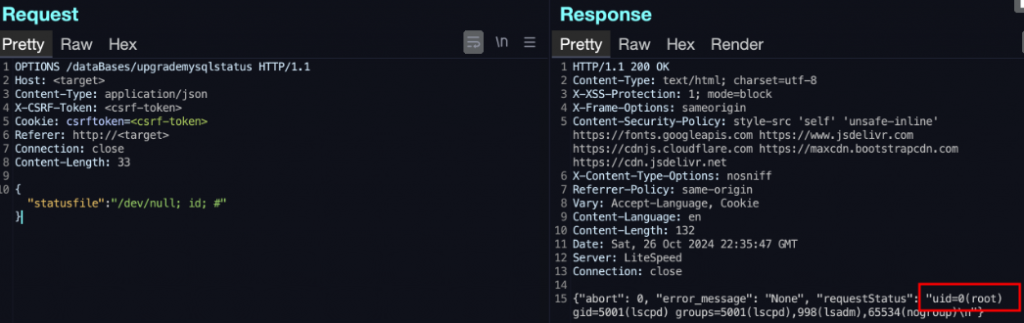
Achieving command execution with root privileges
Source: DreyAnd
DreyAnd created a proof-of-concept exploit demonstrating remote root command execution, showcasing the severity of these vulnerabilities.
“I could only test the exploit on version 2.3.6 as I did not have access to the 2.3.7 version at the time,” DreyAnd
However, given the release date of 2.3.7 (September 19th), before the vulnerabilities were discovered, it was likely also affected.
The PSAUX Ransomware Attack
LeakIX, a threat intelligence search engine, initially reported 21,761 vulnerable CyberPanel instances exposed online, with nearly half located in the United States.
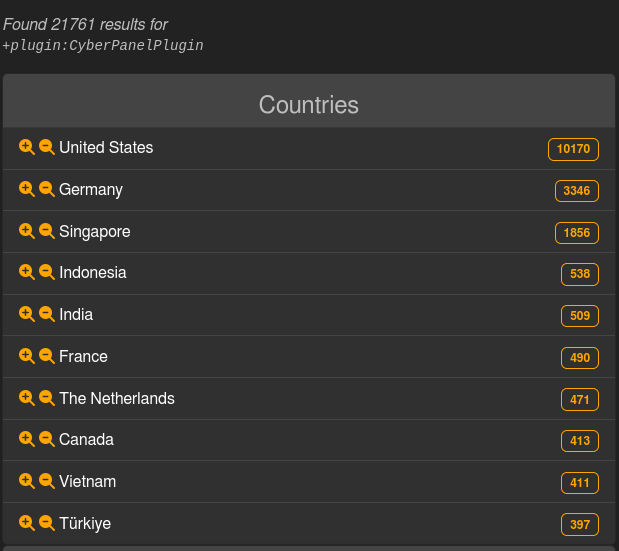
Location of the exposed, vulnerable instances
Source: LeakIX | X
Overnight, however, the number plummeted to around 400, as the compromised servers became inaccessible. This sudden drop strongly suggests a coordinated attack.
Cybersecurity researcher Gi7w0rm tweeted that these instances managed over 152,000 domains and databases, highlighting the scale of the potential impact. LeakIX confirmed that threat actors mass-exploited the vulnerabilities to deploy the PSAUX ransomware.
The PSAUX ransomware, active since June 2024, targets exposed web servers using vulnerabilities and misconfigurations. Upon execution, it encrypts files using a unique AES key and IV, then encrypts these keys with an enclosed RSA key, saving them as /var/key.enc and /var/iv.enc. Ransom notes, named index.html, appear in every folder, and a copy is placed in /etc/motd, displayed upon user login.
LeakIX and Chocapikk obtained the scripts used in the attack, including ak47.py (for exploiting the CyberPanel vulnerability) and actually.sh (for file encryption). Interestingly, a potential weakness in the encryption method is under investigation, potentially offering a path to free decryption.
CyberPanel Response and Mitigation
DreyAnd disclosed the flaw to CyberPanel developers on October 23rd, 2024, with a fix for the authentication issue submitted to GitHub that same evening. While users installing from GitHub or through the upgrade process receive the fix, a new official version or CVE announcement has yet to be released by CyberPanel. BleepingComputer reached out to CyberPanel for comment but is awaiting a response.
Urgent Action Recommended
Due to ongoing exploitation, users are strongly urged to upgrade to the latest CyberPanel version available on GitHub immediately. As of October 29th, 2024, LeakIX released a decryptor; however, users should back up their data before attempting decryption to avoid potential data corruption if the wrong key is used. This PSAUX ransomware attack serves as a stark reminder of the critical importance of timely software updates and robust security practices.