Windows BitLocker Vulnerability (CVE-2025-21210): A Critical Encryption Flaw
A critical Windows BitLocker Vulnerability, CVE-2025-21210, has been discovered in Windows BitLocker’s AES-XTS encryption, exposing it to a novel randomization attack.
This flaw allows attackers with physical access to manipulate ciphertext, resulting in sensitive data being written to the disk in plaintext. This highlights the ongoing evolution of attacks against full-disk encryption.
BitLocker, a mainstay of Windows security, relies on AES-XTS for encrypting storage. Unlike its predecessor, AES-CBC, vulnerable to bit-flipping attacks, AES-XTS theoretically prevents targeted plaintext manipulation through its randomization. However, CVE-2025-21210 proves otherwise.
Understanding the AES-XTS Encryption Flaw
Computer forensics expert Maxim Suhanov explains that the vulnerability stems from a design flaw in BitLocker’s crash dump configurations. By corrupting the registry key (HKLM\System\ControlSet001\Control\CrashControl), attackers can disable the dumpfve.sys crash dump filter driver.
This forces the Windows kernel to write unencrypted hibernation images—containing sensitive data like passwords and encryption keys—directly to the disk. The implications of the Windows BitLocker vulnerability on data security are significant.
How Attackers Exploit CVE-2025-21210 in Full-Disk Encryption
The attack unfolds in two phases: identifying target locations on the disk by observing ciphertext changes across multiple disk states, and then randomizing specific ciphertext blocks to expose plaintext.
This Windows BitLocker Vulnerability poses serious risks, particularly in scenarios involving physical access, such as corporate espionage targeting stolen laptops with TPM-only BitLocker, or data recovery abuse targeting devices sent for repair.
While requiring high technical skill and physical access, the potential for sensitive data exposure from RAM is severe.
Fix Available for CVE-2025-21210: Mitigating Risks Associated with the AES-XTS Vulnerability
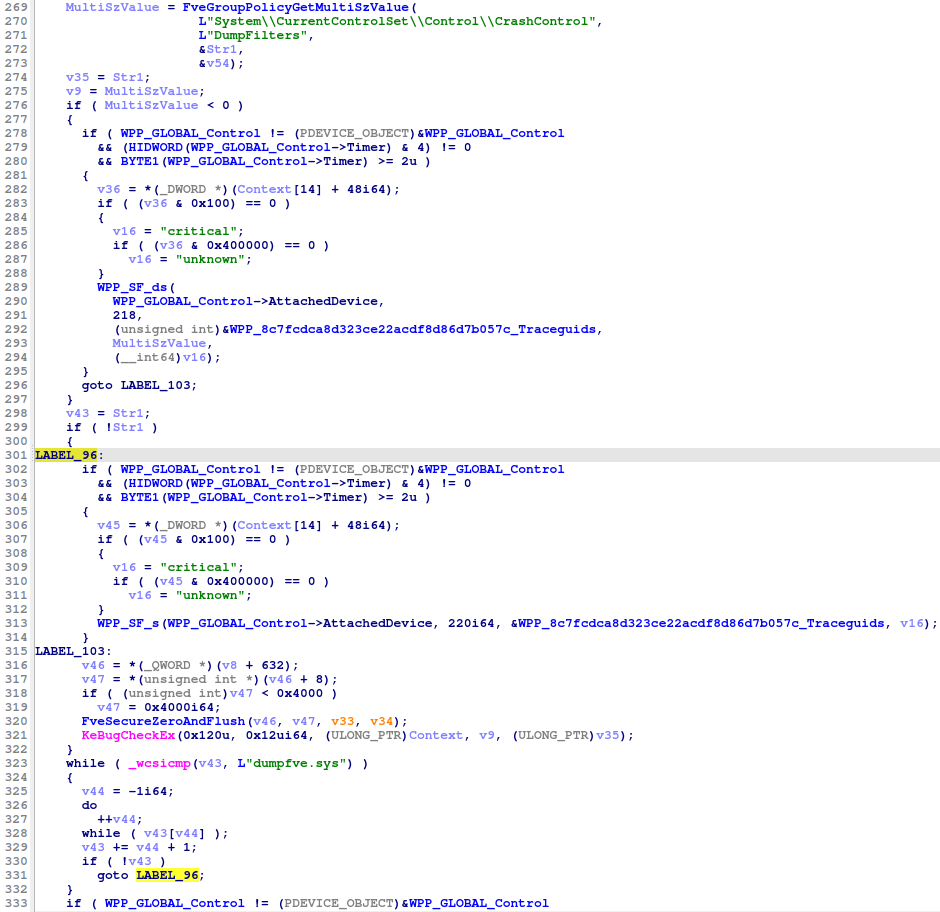
Microsoft has addressed this AES-XTS Vulnerability by releasing an updated fvevol.sys driver. This patch validates the presence of dumpfve.sys in the DumpFilters registry value.
If missing or corrupted, Windows crashes on boot, preventing unencrypted data writes. Applying Microsoft’s security patch for BitLocker is crucial.
The significance of applying this patch cannot be overstated. Users should immediately install the update and implement robust security practices.
Organizations need comprehensive security measures to mitigate risks associated with physical access and cryptographic vulnerabilities.
The importance of physical security for devices using BitLocker, and best practices for securing encrypted data on Windows, are also paramount for enterprise data.
Understanding the attack phases of the BitLocker vulnerability is key to prevention. The potential risks of unencrypted data exposure in corporate environments, and the role of encryption in protecting sensitive information, must be understood to mitigate risks.