PLAYFULGHOST Malware: Sophisticated Cyberattack Utilizing Multiple Vectors
Cybersecurity researchers have uncovered a new and sophisticated malware campaign deploying PLAYFULGHOST, a potent backdoor with extensive data-gathering capabilities. This malware, identified by Google’s Managed Defense team and further analyzed by Mandiant, leverages a multi-pronged attack strategy combining phishing emails, SEO poisoning, and trojanized VPN applications to infect unsuspecting victims. The wide range of functionalities and the sophisticated techniques employed make PLAYFULGHOST a significant threat.
PLAYFULGHOST: Functionality and Infection Vectors
PLAYFULGHOST boasts a comprehensive arsenal of malicious features, including keylogging, screen capture, audio recording, remote shell access, and file transfer/execution capabilities. Its functionality overlaps significantly with the Gh0st RAT, a known remote administration tool whose source code was publicly leaked in 2008.
This suggests a possible link to existing malicious actors or the adaptation of previously known techniques. The malware’s ability to gather extensive data, including keystrokes, screenshots, audio recordings, QQ account information, installed security software details, clipboard content, and system metadata, presents a serious threat to data security and privacy.
The initial infection vectors are particularly noteworthy. PLAYFULGHOST is distributed through two primary methods:
- Phishing Emails: Malicious RAR archives, disguised as image files (.jpg extension), are attached to phishing emails. These emails often employ lures related to codes of conduct, aiming to trick users into opening the attachments. Once extracted and executed, the archive releases a malicious Windows executable that downloads and executes PLAYFULGHOST from a remote server. Google’s Managed Defense team described one such case, stating, “In one phishing case, the infection begins by tricking the victim into opening a malicious RAR archive disguised as an image file by using a .jpg extension. When extracted and executed by the victim, the archive drops a malicious Windows executable, which eventually downloads and executes PLAYFULGHOST from a remote server.”
- SEO Poisoning: This method involves manipulating search engine results to promote malicious links. Unsuspecting users searching for legitimate VPN applications, specifically LetsVPN in this instance, are directed to download malware-laced installers. Upon execution, these installers drop an interim payload responsible for retrieving and installing the PLAYFULGHOST backdoor components. This highlights the importance of verifying the legitimacy of downloaded software from trusted sources.
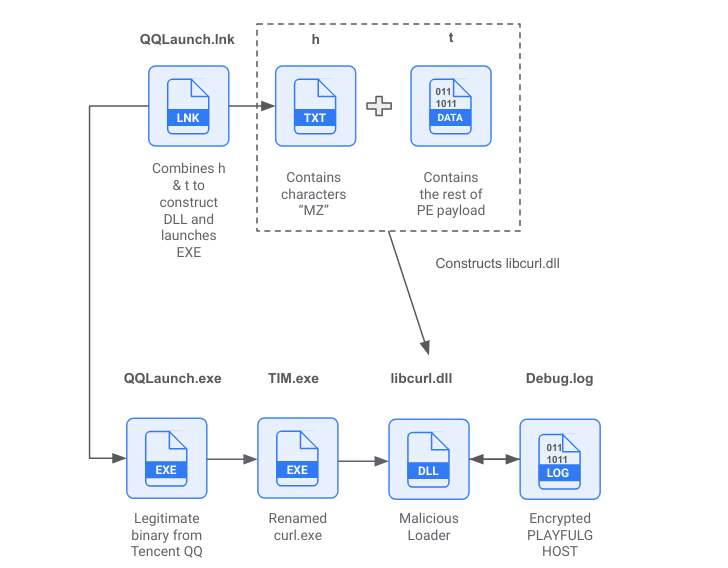
The infection process itself is sophisticated, employing techniques like DLL search order hijacking and side-loading. Mandiant observed a particularly advanced execution scenario involving a Windows shortcut file (“QQLaunch.lnk”) that combines the contents of two other files to create a malicious DLL, which is then side-loaded using a renamed version of “curl.exe.” This demonstrates the attackers’ advanced knowledge of Windows system internals.
Persistence and Additional Capabilities of PLAYFULGHOST
PLAYFULGHOST establishes persistence on the compromised system through four distinct methods: Run registry key modification, scheduled task creation, placement within the Windows Startup folder, and the installation of a Windows service. This ensures the malware’s continued presence and operation, even after a system reboot.
Beyond data exfiltration, PLAYFULGHOST offers additional malicious capabilities, including the ability to drop further payloads, block user input, clear Windows event logs, wipe clipboard data, manipulate files, delete browser caches and profiles (targeting Sogou, QQ, 360 Safety, Firefox, and Google Chrome), erase messaging application profiles and local storage (Skype, Telegram, and QQ), and deploy additional tools such as Mimikatz and a rootkit capable of hiding registry entries, files, and processes.
The inclusion of Terminator, an open-source utility, allows for the termination of security processes through BYOVD (Bring Your Own Vulnerable Driver) attacks. Mandiant also noted an instance of PLAYFULGHOST being embedded within BOOSTWAVE, a shellcode acting as an in-memory dropper for an appended Portable Executable (PE) payload.
PLAYFULGHOST Targeting Specific Apps in a Well Rounded and Planned Campaign
The targeting of applications like Sogou, QQ, and 360 Safety, coupled with the use of LetsVPN as a lure, suggests a focus on Chinese-speaking Windows users. This is reminiscent of a similar campaign in July 2024, reported by eSentire, which used fake Google Chrome installers to spread Gh0st RAT via a dropper called Gh0stGambit.
The combination of phishing, SEO poisoning, and trojanized VPN apps demonstrates a well-coordinated and multifaceted attack strategy. The extensive data-gathering capabilities of PLAYFULGHOST, combined with its persistence mechanisms and additional malicious tools, pose a significant risk to affected users.
Summary
The PLAYFULGHOST malware campaign highlights the evolving sophistication of cyberattacks and the importance of robust cybersecurity practices. Users should be vigilant against phishing emails, carefully verify the legitimacy of software downloads, and implement strong security measures to protect against these types of threats. The use of SEO poisoning as a distribution vector emphasizes the need for caution even when searching for seemingly legitimate software. The ongoing evolution of malware necessitates a proactive and adaptable approach to cybersecurity.